In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents have emerged as pivotal players in revolutionizing how we interact with machines and data. These intelligent entities are transforming industries and driving innovation, making it crucial for businesses and individuals to understand their core components and applications. This article delves into the world of AI agents, exploring their architecture, components, and practical use cases across various sectors
Table of Contents

What are AI Agents?
AI agents are sophisticated software programs designed to perform tasks autonomously. Unlike traditional software, these agents possess the ability to learn, adapt, and make decisions based on the data they process. From personal assistants like Siri and Alexa to complex systems managing financial portfolios, AI agents are becoming integral to our everyday existence.
Let’s breakdown it in simpler terms:
- It’s AI-powered : It uses artificial intelligence to understand, reason and make decisions.
- It has Goals : It’s designed to achieve something, whether it’s answering a customer’s question, booking a flight, or even controlling a robot.
- It acts autonomously : Once given a goal, it can work independently, figuring out the best way to achieve it.
- It learns and adapts: Many AI agents can learn from their experiences and improve their performance over time, becoming more efficient at their tasks.
- It can interact with the environment: This could be through a user interface, like a chat window, or by interacting with other systems and data sources.
Agent Components
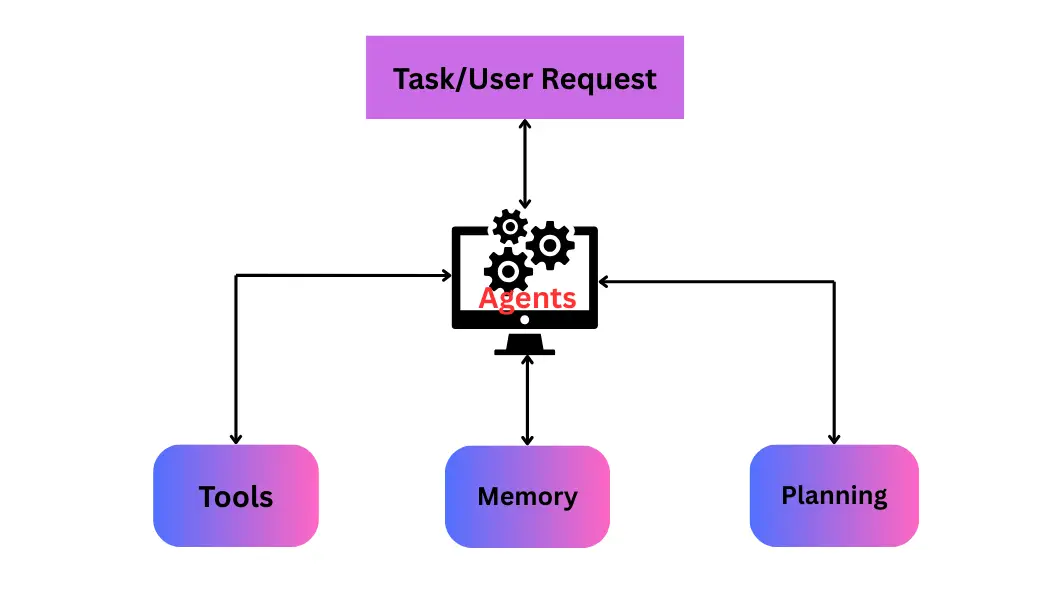
AI agents require three fundamental capabilities to effectively tackle complex tasks: planning abilities, tool utilization, and memory management. Let’s dive into how these components work together to create functional AI agents.
1. Planning: The Brain of the Agent
At the core of any effective AI agent is its planning capability, powered by large language models (LLMs). Modern LLMs enable several crucial planning functions:
1. Task decomposition through chain-of-thought reasoning
2. Self-reflection on past actions and information
3. Adaptive learning to improve future decisions
4. Critical analysis of current progress
While current LLM planning capabilities aren’t perfect, they’re essential for task completion. Without robust planning abilities, an agent cannot effectively automate complex tasks, which defeats its primary purpose.
2. Tool Utilization: Extending the Agent’s Capabilities
The second critical component is an agent’s ability to interface with external tools. A well-designed agent must not only have access to various tools but also understand when and how to use them appropriately. Common tools include:
1. Code interpreters and execution environments
2. Web search and scraping utilities
3. Mathematical calculators
4. Image generation systems
These tools enable the agent to execute its planned actions, turning abstract strategies into concrete results. The LLM’s ability to understand tool selection and timing is crucial for handling complex tasks effectively.
3. Memory Systems: Retaining and Utilizing Information
The third essential component is memory management, which comes in two primary forms:
a) Short-term (Working) Memory
- Functions as a buffer for immediate context
- Enables in-context learning
- Sufficient for most task completions
- Helps maintain continuity during task iteration
b) Long-term Memory
- Implemented through external vector stores
- Enables fast retrieval of historical information
- Valuable for future task completion
- Less commonly implemented but potentially crucial for future developments
- Memory systems allow agents to store and retrieve information gathered from external tools, enabling iterative improvement and building upon previous knowledge.
AI Agents use case across different Industries
AI agents are revolutionizing industries by automating processes, enhancing decision-making, and providing insights that drive innovation. Some notable use cases include:
- Healthcare: AI agents assist in diagnosing diseases, personalizing treatment plans, and managing patient records, improving outcomes and efficiency.
- Finance: In the financial sector, AI agents analyze market trends, predict stock movements, and manage risk assessments, enabling smarter investment strategies.
- Retail: AI agents enhance customer experiences through personalized recommendations, dynamic pricing strategies, and efficient inventory management.
- Manufacturing: AI agents optimize production lines, predict maintenance needs, and ensure quality control, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles and traffic management systems use AI agents to improve safety, reduce congestion, and enhance route planning.
In conclusion, AI agents are at the forefront of technological advancement, driving efficiency and innovation across diverse sectors. By understanding their components and architecture, businesses can harness their potential to transform operations and deliver exceptional value. As AI agents continue to evolve, their role in shaping the future of industries is set to become even more significant.


Pingback: Various types of AI Agents: A Comprehensive Guide – Skillplayground