Artificial Intelligence (AI) has undergone significant advancements over the years, revolutionizing how we interact with technology. One of the latest innovations in this field is Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which promises to transform information retrieval by adding a layer of autonomy and intelligence to traditional systems. This article explores the concept of Agentic RAG, its limitations, architecture, benefits, and comparision between traditional RAG and Agentic RAG
Table of Contents

What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
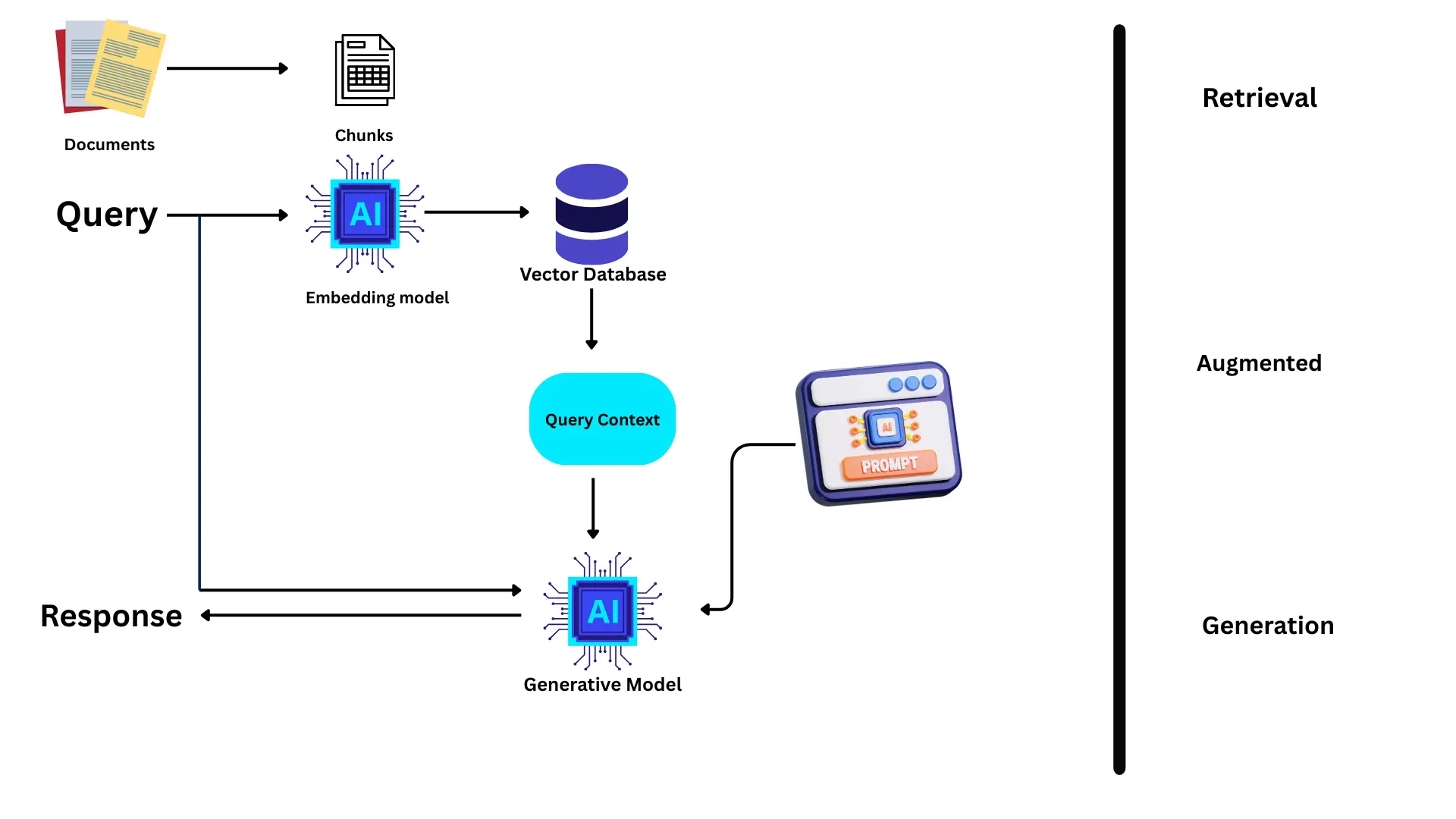
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique for building LLM-powered applications. It leverages an external knowledge source to provide the LLM with relevant context and reduce hallucinations.
A naive RAG pipeline consists of a retrieval component (typically composed of an embedding model and a vector database) and a generative component (an LLM). At inference time, the user query is used to run a similarity search over the indexed documents to retrieve the most similar documents to the query and provide the LLM with additional context.
Limitation of RAG
1. Lack of Multifunctionality: The naive RAG pipeline only considers one external knowledge source. However, some solutions might require two external knowledge sources, and some solutions might require external tools and APIs, such as web searches.
2. Dependence on Data Organization: The effectiveness of RAG is heavily influenced by how well the underlying data is organized. Poorly structured data can hinder the retrieval process, making it difficult for the system to surface the most useful documents.
3. Broad Matching Criteria: RAG systems may match queries based on broad similarities rather than specific details, resulting in the retrieval of documents that do not capture the nuances of the query. This can lead to a lack of precision in the information provided.
4. Lack of Iterative Reasoning: RAG systems struggle with iterative reasoning capabilities. They may retrieve data that is semantically similar to a query but fail to determine if it is the most relevant information needed to solve a specific problem. This can lead to irrelevant or less useful results.
What is Agentic RAG?
Agentic RAG builds upon the traditional RAG framework by introducing autonomous AI agents that refine and optimize the retrieval and generation processes. These agents actively analyze, filter, and validate retrieved information, improving accuracy and contextual relevance.
Agentic RAG represents a significant evolution from traditional RAG by introducing dynamic agents capable of real-time planning, execution, and optimization of query processes. This shift from static, rule-based systems to adaptive, intelligent frameworks enables more effective handling of complex queries and adapting to evolving information landscapes.
Key Features of Agentic RAG
- Adaptive reasoning: At its core, agentic RAG employs a “reasoner” that interprets user intent, develops strategic plans for information retrieval, and evaluates the reliability of data sources. This component adapts in real-time, pivoting to different sources as needed to enhance the quality and precision of information provided.
- Collaborative agent network: Agentic RAG utilizes a network of specialized agents that function like a team of experts with distinct skills. This collaborative approach allows for effective scaling and the ability to handle extensive and diverse datasets.
- Dynamic planning and execution: Unlike static, rule-based systems, agentic RAG introduces dynamic agents capable of real-time planning, execution, and optimization of query processes. This shift enables more effective handling of complex queries and adaptation to evolving information landscapes.
- Enhanced retrieval techniques:
- Advanced reranking algorithms and hybrid search methodologies refine search precision.
- Multiple vectors per document improve content representation and relevance identification.
- Semantic caching reduces computational costs and ensures consistent responses for similar queries.
- Multimodal integration extends capabilities beyond text, incorporating images and other data types for more comprehensive responses.
- Intelligent quality control: Agentic RAG agents not only retrieve data but also evaluate, correct, and verify the information gathered. This ensures accurate and reliable outputs, filtering out extraneous or unreliable information.
- External tool integration: These agents can utilize a variety of external tools and resources, including search engines, databases, and specialized APIs, to enhance their information gathering and processing capabilities.
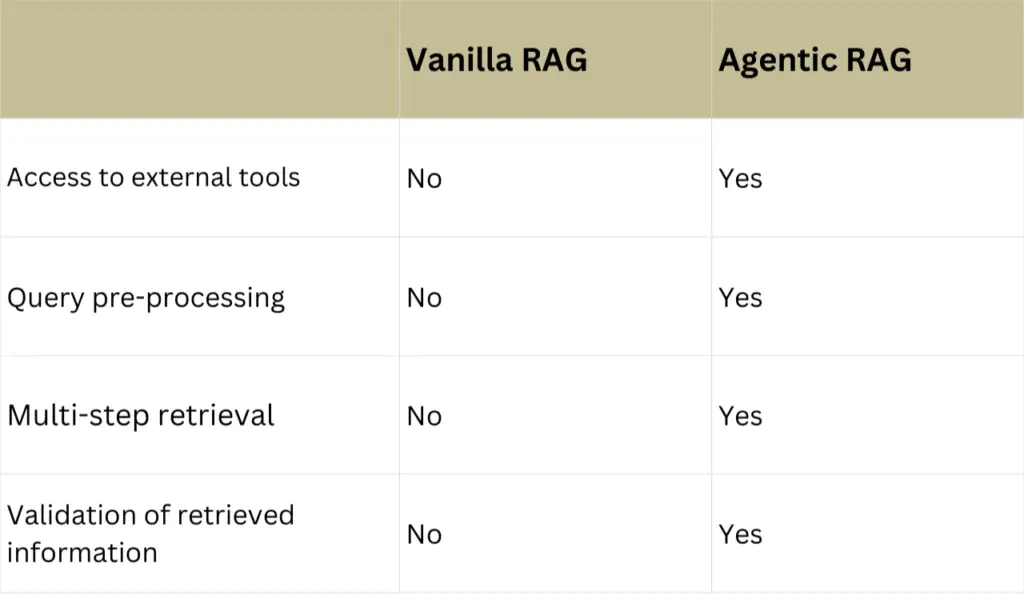
Agentic RAG Vs Vanila RAG
Future Application and Benefits of Agentic RAG
The potential applications of agentic RAG span various industries and functions:
- Customer and employee service: Handling complex inquiries with personalized, accurate responses.
- Intelligent assistants: Providing more natural, context-aware interactions.
- Scientific research: Synthesizing vast amounts of data to generate new hypotheses and insights.
- Content creation: Assisting writers and marketers in generating relevant, high-quality content.
- Education: Tailoring learning experiences to individual student needs.
- Healthcare: Supporting medical professionals with up-to-date information while maintaining patient privacy.
- Legal services: Aiding in legal research, case preparation, and compliance monitoring.